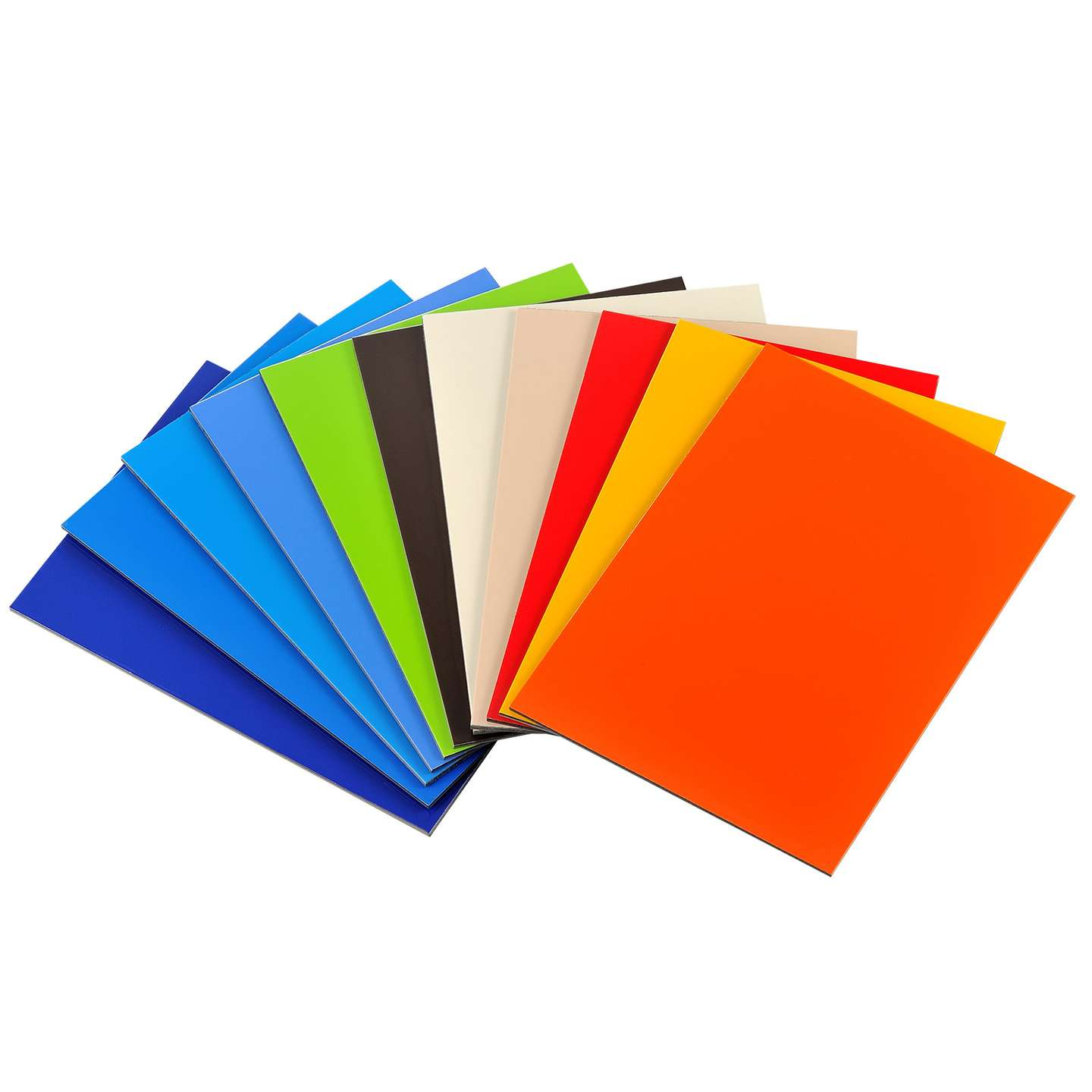
When you stand before the facades of shopping malls, subway station advertising walls, or modern building curtain walls, and see those smooth, colorful, and textured panels, a significant portion of them are aluminum composite panels (ACP). With its excellent decorative effect and stable overall performance, ACP has become one of the most widely used materials in the field of building decoration.
ACP is a multi-layered structural material produced on specialized equipment. Its surface layer uses chemically treated and coated aluminum sheets, combining strength and decoration; the core material is polyethylene (PE), giving the panel good toughness and processing performance. This structure achieves a good balance between weight, strength, flatness, and aesthetics.
ACP was first successfully developed in 1968 by Alusuisse and BASF in Germany, and went into production the following year. Its well-known brand "Alucobond®" quickly established a reputation in the international market. Aluminum composite panels (ACPs) entered the Chinese market in the 1990s and, thanks to their advantages such as lightweight, high strength, good weather resistance, and convenient construction, have been widely used in building curtain walls, interior decoration, and advertising signage.
The Structural Composition of ACPs: Key Factors Determining Quality
While the name suggests ACPs are composed of "aluminum" and "plastic," their accurate name is aluminum-plastic composite panel, a high-performance panel made of multiple materials. A typical structure consists of two layers of high-purity aluminum alloy sheets, with a non-toxic low-density polyethylene (PE) core sheet in the middle, and a protective film on the front. Depending on the application environment, the surface coating of ACPs varies: outdoor panels typically use a fluorocarbon resin (PVDF) coating, while indoor panels can use a non-fluorocarbon resin coating.
1. Aluminum Sheets Commonly used aluminum materials for ACPs include 1100H18 (pure aluminum), 3003H16 (aluminum-manganese alloy), and 5005H14 (aluminum-magnesium alloy). Different aluminum materials vary in strength, fatigue resistance, and processing performance. 1100 pure aluminum is slightly inferior to 3003 and 5005 aluminum alloys in shear strength and fatigue strength, while alloy aluminum materials have advantages in structural stability and service life.
2. Polyethylene (PE) Core Material Ordinary aluminum composite panels typically use high-pressure low-density polyethylene resin as the core material. The melt index of polyethylene has a significant impact on the penetration resistance, flexural strength, and shear strength of the panel. Polyethylene with an excessively high melt index is not suitable as a core material, as it will significantly affect the overall performance of the panel.
3. Surface Coating Common aluminum composite panel coatings include fluorocarbon coatings (PVDF), polyester coatings (PE), and acrylic coatings (AC). PVDF coatings have excellent weather resistance and corrosion resistance, with a normal service life of over 20 years; polyester coatings are generally suitable for 8–10 years of use; and acrylic coatings are mostly used for short-term applications of 3–5 years. According to national standards, aluminum composite panels (ACPs) for building exterior walls must use a PVDF fluorocarbon coating with a resin content of no less than 70% to ensure long-term weather resistance.
4. Polymer Adhesive Film: The polymer film, located between the aluminum sheet and the plastic core material, plays a crucial adhesive role and is one of the core materials ensuring the structural stability and durability of the panel.
5. Protective Film: The protective film covering the surface of the ACP protects the panel surface during production, transportation, storage, processing, and installation, preventing scratches and contamination, and ensuring the final appearance.
Synergistic Material Combinations for Superior Performance
ACPs are based on an aluminum sheet and a plastic core: the aluminum sheet primarily provides support and decoration, while the plastic core provides cushioning, protection, and stability. Combined with surface coatings and functional films, the panels simultaneously possess multiple advantages such as antistatic properties, oxidation resistance, strong weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal, meeting the comprehensive needs of modern architecture for safety, durability, and design.